【Arduino】Parallax HB-25 Motor Controlを使ってみるよ
プログラム
こちらに素晴らしい先駆者がいました。
Reefwing Robotics: Parallax HB-25 Motor Control Library for Arduino
Servo.hを使ってコントロールをしていきます。
私が使ったコードはこちら
#include <Servo.h>
#define REVERSE 1000
#define STOP 1500
#define FORWARD 2000
#define HOLD_OFF_TIME 8
#define controlPin 9
Servo servo;
void setup(){
// HB-25 initialisation time (5ms)
delay(5);
pinMode(controlPin, OUTPUT);
// Set control pin low on power up
digitalWrite(controlPin, LOW);
//serial confirm
Serial.begin(9600);
}
void loop(){
// Attach HB-25 to the control pin & set valid range
servo.attach(controlPin, 800, 2200);
servo.writeMicroseconds(STOP);
Serial.println("Stop");
delay(5000);
// Attach HB-25 to the control pin & set valid range
servo.attach(controlPin, 800, 2200);
servo.writeMicroseconds(FORWARD);
Serial.println("Forward");
delay(5000);
// Attach HB-25 to the control pin & set valid range
servo.attach(controlPin, 800, 2200);
servo.writeMicroseconds(STOP);
Serial.println("Stop");
delay(5000);
// Attach HB-25 to the control pin & set valid range
servo.attach(controlPin, 800, 2200);
servo.writeMicroseconds(REVERSE);
Serial.println("Reverse");
delay(5000);
}
結果
| コマンド | M1 | M2 |
|---|---|---|
| STOP | 0 | 0 |
| FORWARD | + | - |
| REVERSE | - | + |
今回は可変電源から6V流したので、6Vが出力されています。
コマンドによって、電源の流れる向きが制御できます。
【赤外線温度センサ】MLX90614を複数個使ってみる。(Arduino)
赤外線温度センサを2つ使ってみるよ。
このMLX90614の赤外線温度センサはI2Cで温度を取得する際に、
アドレスが同じなので、このままでは複数個つなげられない。
そこで、MLX90164のアドレスを一つ書き替えたいと思います。
こちらのArudinoフォーラムを参考にすると、
以下のプログラムをArduinoに書き込み、
一つのMLX90614のみをつなげてアドレスを書き代える事ができるようです。(Connecting Infrared Thermometer MLX90614 to Wiring - Wiring参考)
※i2cmaster.hを持っていないときはgithub
Arduino Playground - I2cScanner
で入手可能
#include "i2cmaster.h"
// Pins: Standard: SDA:A4 SCL:A5
// Mega: SDA:D20 SCL:D21
byte MLXAddr = 0x5A<<1; // Default address
//byte MLXAddr = 0; // Universal address
void setup(){
Serial.begin(9600);
Serial.println("Setup...");
i2c_init(); //Initialise the i2c bus
PORTC = (1 << PORTC4) | (1 << PORTC5); //enable pullups
delay(5000); // Wait to allow serial connection
ReadAddr(0); // Read current address bytes
ChangeAddr(0x55, 0x00); // Change address to new value
//ChangeAddr(0x5A, 0xBE); // Change address to default value
ReadAddr(0); // Read address bytes
delay(5000); // Cycle power to MLX during this pause
ReadTemp(0); // Read temperature using default address
ReadTemp(MLXAddr); // Read temperature using new address
}
void loop(){
delay(1000); // wait a second
}
word ChangeAddr(byte NewAddr1, byte NewAddr2) {
Serial.println("> Change address");
i2c_start_wait(0 + I2C_WRITE); //send start condition and write bit
i2c_write(0x2E); //send command for device to return address
i2c_write(0x00); // send low byte zero to erase
i2c_write(0x00); //send high byte zero to erase
if (i2c_write(0x6F) == 0) {
i2c_stop(); //Release bus, end transaction
Serial.println(" Data erased.");
}
else {
i2c_stop(); //Release bus, end transaction
Serial.println(" Failed to erase data");
return -1;
}
Serial.print(" Writing data: ");
Serial.print(NewAddr1, HEX);
Serial.print(", ");
Serial.println(NewAddr2, HEX);
for (int a = 0; a != 256; a++) {
i2c_start_wait(0 + I2C_WRITE); //send start condition and write bit
i2c_write(0x2E); //send command for device to return address
i2c_write(NewAddr1); // send low byte zero to erase
i2c_write(NewAddr2); //send high byte zero to erase
if (i2c_write(a) == 0) {
i2c_stop(); //Release bus, end transaction
delay(100); // then wait 10ms
Serial.print("Found correct CRC: 0x");
Serial.println(a, HEX);
return a;
}
}
i2c_stop(); //Release bus, end transaction
Serial.println("Correct CRC not found");
return -1;
}
void ReadAddr(byte Address) {
Serial.println("> Read address");
Serial.print(" MLX address: ");
Serial.print(Address, HEX);
Serial.print(", Data: ");
i2c_start_wait(Address + I2C_WRITE); //send start condition and write bit
i2c_write(0x2E); //send command for device to return address
i2c_rep_start(Address + I2C_READ);
Serial.print(i2c_readAck(), HEX); //Read 1 byte and then send ack
Serial.print(", ");
Serial.print(i2c_readAck(), HEX); //Read 1 byte and then send ack
Serial.print(", ");
Serial.println(i2c_readNak(), HEX);
i2c_stop();
}
float ReadTemp(byte Address) {
int data_low = 0;
int data_high = 0;
int pec = 0;
Serial.println("> Read temperature");
Serial.print(" MLX address: ");
Serial.print(Address, HEX);
Serial.print(", ");
i2c_start_wait(Address + I2C_WRITE);
i2c_write(0x07); // Address of temp bytes
// read
i2c_rep_start(Address + I2C_READ);
data_low = i2c_readAck(); //Read 1 byte and then send ack
data_high = i2c_readAck(); //Read 1 byte and then send ack
pec = i2c_readNak();
i2c_stop();
//This converts high and low bytes together and processes temperature, MSB is a error bit and is ignored for temps
float Temperature = 0x0000; // zero out the data
// This masks off the error bit of the high byte, then moves it left 8 bits and adds the low byte.
Temperature = (float)(((data_high & 0x007F) << 8) + data_low);
Temperature = (Temperature * 0.02) - 273.16;
Serial.print(Temperature);
Serial.println(" C");
return Temperature;
}書き換え後に、もう一つのMLX90614をつないで、
I2CScannerで値の確認をしてみます。
以下は公式からgetしました。
I2CScanner
// --------------------------------------
// i2c_scanner
//
// Version 1
// This program (or code that looks like it)
// can be found in many places.
// For example on the Arduino.cc forum.
// The original author is not know.
// Version 2, Juni 2012, Using Arduino 1.0.1
// Adapted to be as simple as possible by Arduino.cc user Krodal
// Version 3, Feb 26 2013
// V3 by louarnold
// Version 4, March 3, 2013, Using Arduino 1.0.3
// by Arduino.cc user Krodal.
// Changes by louarnold removed.
// Scanning addresses changed from 0...127 to 1...119,
// according to the i2c scanner by Nick Gammon
// http://www.gammon.com.au/forum/?id=10896
// Version 5, March 28, 2013
// As version 4, but address scans now to 127.
// A sensor seems to use address 120.
// Version 6, November 27, 2015.
// Added waiting for the Leonardo serial communication.
//
//
// This sketch tests the standard 7-bit addresses
// Devices with higher bit address might not be seen properly.
//
#include <Wire.h>
void setup()
{
Wire.begin();
Serial.begin(9600);
while (!Serial); // Leonardo: wait for serial monitor
Serial.println("\nI2C Scanner");
}
void loop()
{
byte error, address;
int nDevices;
Serial.println("Scanning...");
nDevices = 0;
for(address = 1; address < 127; address++ )
{
// The i2c_scanner uses the return value of
// the Write.endTransmisstion to see if
// a device did acknowledge to the address.
Wire.beginTransmission(address);
error = Wire.endTransmission();
if (error == 0)
{
Serial.print("I2C device found at address 0x");
if (address<16)
Serial.print("0");
Serial.print(address,HEX);
Serial.println(" !");
nDevices++;
}
else if (error==4)
{
Serial.print("Unknow error at address 0x");
if (address<16)
Serial.print("0");
Serial.println(address,HEX);
}
}
if (nDevices == 0)
Serial.println("No I2C devices found\n");
else
Serial.println("done\n");
delay(5000); // wait 5 seconds for next scan
}
結果

I2Cのアドレスを2つ認識しています。
では、早速2つのMLX90614から温度を取得するプログラムを作ります。
続きにプログラムを載せました。
【Arduino】放射温度センサMLX90614を使ってみる(Galileo2についても解説)
手の温度を取得するために、放射温度センサMLX90614を使ってみる。
用意するもの
手順
- 以下のサイトからライブラリをダウンロードして、Arduino > Libraries にコピーして入れる。
https://github.com/adafruit/Adafruit-MLX90614-Library
- IDEを開き、ファイル→スケッチの例から「Adafruit MLX90614 Library」を選択して、mlxtest.ioを実行する。
結果

補足
- Galileo2の利用について
Galileo2で試してみたところ、どうしてもうまくいきませんでした。
I2Cのポートをうまく認識せず、クロック数の相性があるのでしょうか。
2日取り組みましたが、よくわからないままでした。
- 1つのボードによる複数利用について
以下のサイトから、データシートを読みます。
https://learn.sparkfun.com/tutorials/mlx90614-ir-thermometer-hookup-guide
Every MLX90614 has a default I2C address of 0x5A, but that address can be re-written – one of the major features supported by the device. By reconfiguring the address of an MLX90614, you can add multiple devices (up to 127!) to the same bus to get a larger temperature map.
One last bit to note about the SMBus interface – every read or write transmission should be completed with an 8-bit CRC (CRC-8-CCITT) check using a x8+x2+x1+x0 polynomial – handy for that extra bit of data-confidence.
複数つなげる事が可能みたいですね。
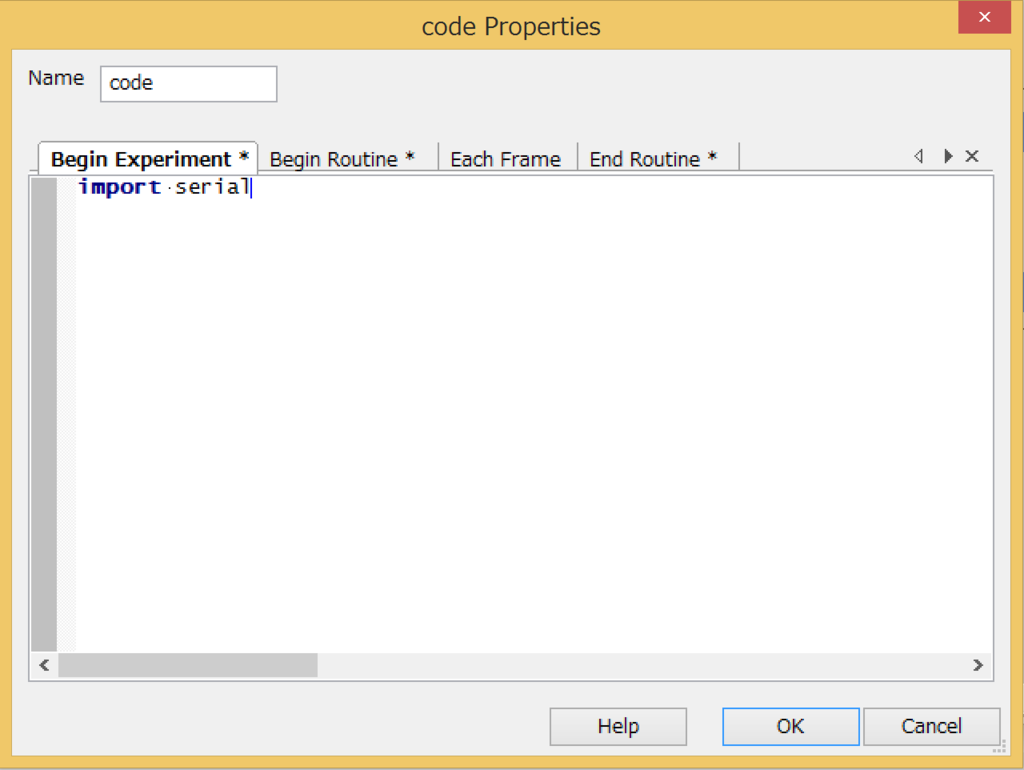
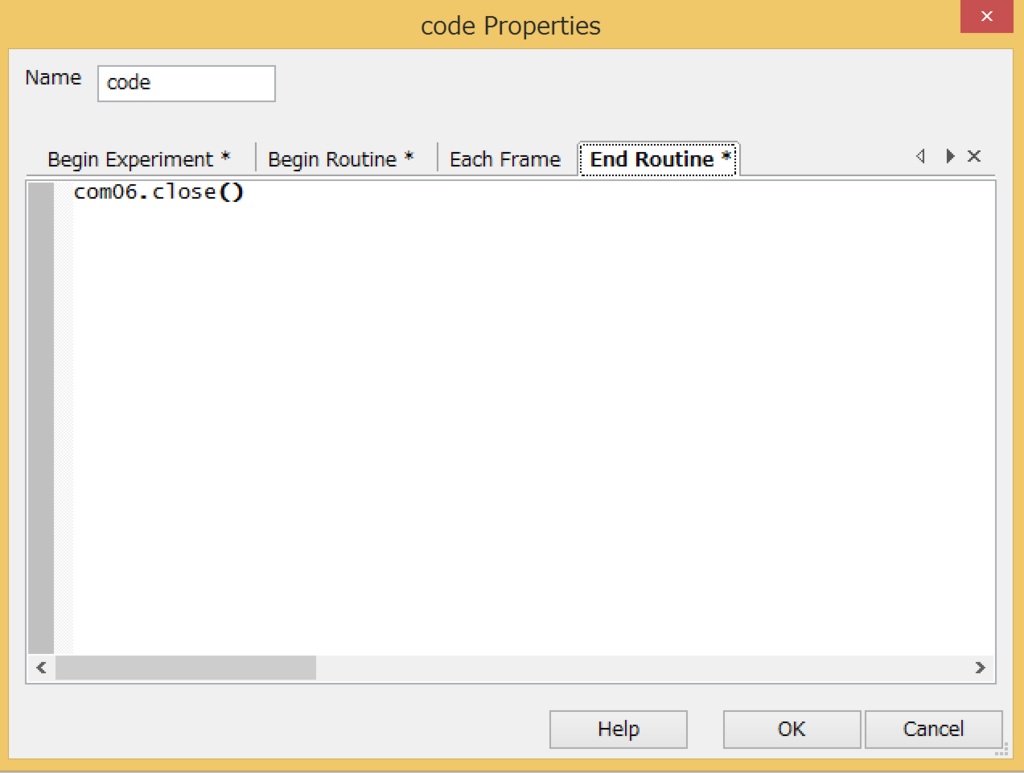
【PsychoPy】Arduinoとシリアル通信をさせる。
Adruino(Galileoとのシリアル通信)をBuilder modeでする。
作成したもの
- PsychoPy側から、文字列(一行)を送信
- Arduino側で受け取ったら、その値をPC側に送信
- PsychoPyのプログラムにて、表示
コード
Arduino側
#define num 30//一度に送れる文字数
void setup() {
Serial.begin(9600);//シリアル通信開始
}
void loop() {
char incomingByte = 0; // 受信データ用
char sended_value[num] = {0};
int i = 0;
//シリアル通信
while(1){
if(Serial.available() > 0){
incomingByte = Serial.read(); // 受信データを読み込む
if(incomingByte > 47 && incomingByte < 59 ){ //アスキーコード10進数(47~59がきたら読み込み)
sended_value[i] = incomingByte;//配列に入れる
Serial.print(sended_value[i]);
i++;
}
if(incomingByte == '.'){Serial.print(".");}
if(incomingByte == ';'){Serial.println(";");break;}//;が来たらwhile文終了。
}
else{break;}
}
}※ 注意
本Arduino Programはパソコン側から「0,1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9」「",",";"」しか受信をせず
。「;」を受信するとそこまでが1行とみなされる。
一回に受信できるコードは一行まで。
結果

【Arduino(Gallileo2)】シリアル通信 PCから送られてきた値配列に格納・表示
ほんの忘備録です。
PCから値送信→Arduino受信→配列に格納
コード
#define num 30//一度に送れる文字数
void setup() {
Serial.begin(9600);//シリアル通信開始
}
void loop() {
char incomingByte = 0; // 受信データ用
char sended_value[num] = {0};
int i = 0;
//シリアル通信
while(1){
if(Serial.available() > 0){
incomingByte = Serial.read(); // 受信データを読み込む
if(incomingByte > 47 && incomingByte < 59 ){ //アスキーコード10進数(47~59がきたら読み込み)
sended_value[i] = incomingByte;//配列に入れる
Serial.print(sended_value[i]);
i++;
}
if(incomingByte == ';'){Serial.println(";");break;}//;が来たらwhile文終了。
}
}
}
結果

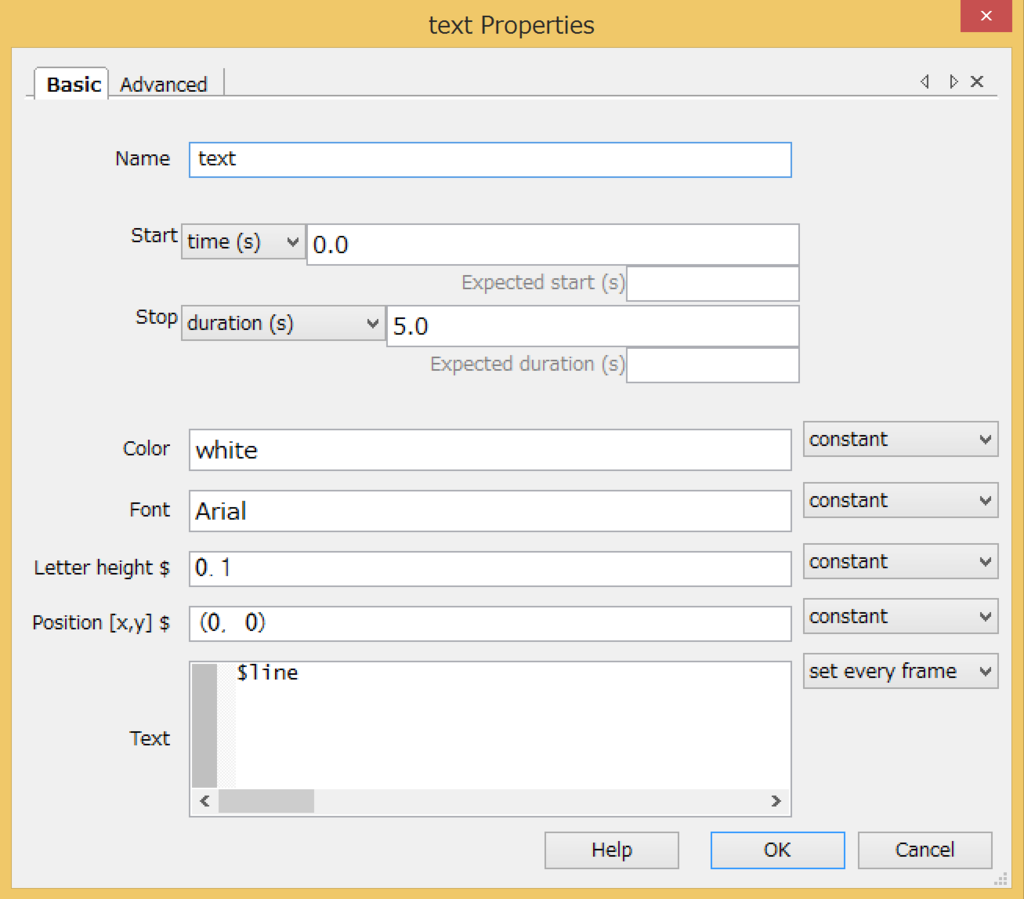
【PsychoPy】Galileo2(Arduino)とシリアル通信をしてみる。(coder編)
本日の朝、動作を確認しました。
Galileo側にコンパイル、スケッチを書き込み後、
PsychoPyのcoderモードで動作を確認しました。
以下が、Galileo側のプログラム
//------------------------------------------
//Tact switch time (P/N: 611 - PTS635SL50LFS)
//------------------------------------------
unsigned long tt, tt2, tt3;
int b_pin = 2; // Desital pin
int ledpin = 13;
int state = 0; // pin state
int flag = 0;
float tt4;
void setup() {
Serial.begin(9600);
pinMode(b_pin, INPUT); // input setting
pinMode(ledpin, OUTPUT); // input setting
digitalWrite(ledpin, LOW); // LED pin
}
void loop() {
float ans , temp , tv ;
float ans2 , temp2 , tv2 ;
state = digitalRead(b_pin); // read data
ans = analogRead(0) ; // read sensor from A0 pin
ans2 = analogRead(1) ; // read sensor from A1 pin
if(state == 1 && flag == 0){
flag = 1;
tt = millis();
Serial.println("ON");
digitalWrite(ledpin, HIGH);
}
if(state == 0 && flag == 1){
tv = (ans*5)/1024; // convert sensor value to voltage
tv2 = (ans2*5)/1024; // convert sensor value to voltage
temp = 100 * (tv - 0.5); // convert voltage to temperature
temp2 = 100 * (tv2 - 0.5); // convert voltage to temperature
tt3 = millis();
tt2 = tt3 -tt;
tt4 = (float)tt2 / 1000;
flag = 0;
Serial.print("time:"); // output serial monitor
Serial.print(tt4); // output serial monitor
Serial.print(",coldbar:"); // output serial monitor
Serial.print(temp); // output serial monitor
Serial.print(",warmbar:"); // output serial monitor
Serial.println(temp2); // output serial monitor
digitalWrite(ledpin, LOW);
}
delay(100);
}以下がPsychoPyのcoder側のプログラム。
import serial
com06 = serial.Serial('COM6') # open first serial port COM6
line = com06.readline() # read a '\n' terminated line
print(line)
com06.close()Galileo2はCOM6につないである。
実行結果
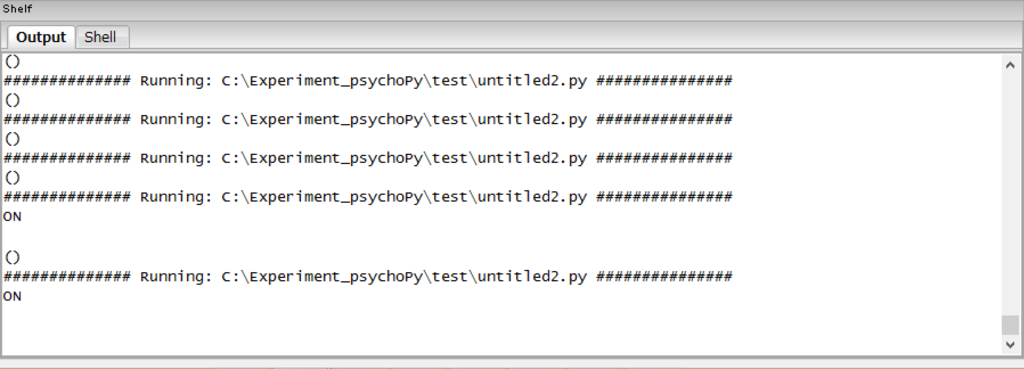
次はviewerモードで実装してみます!